A&P: Levels of structural organization
Levels of Structural Organization in the human body
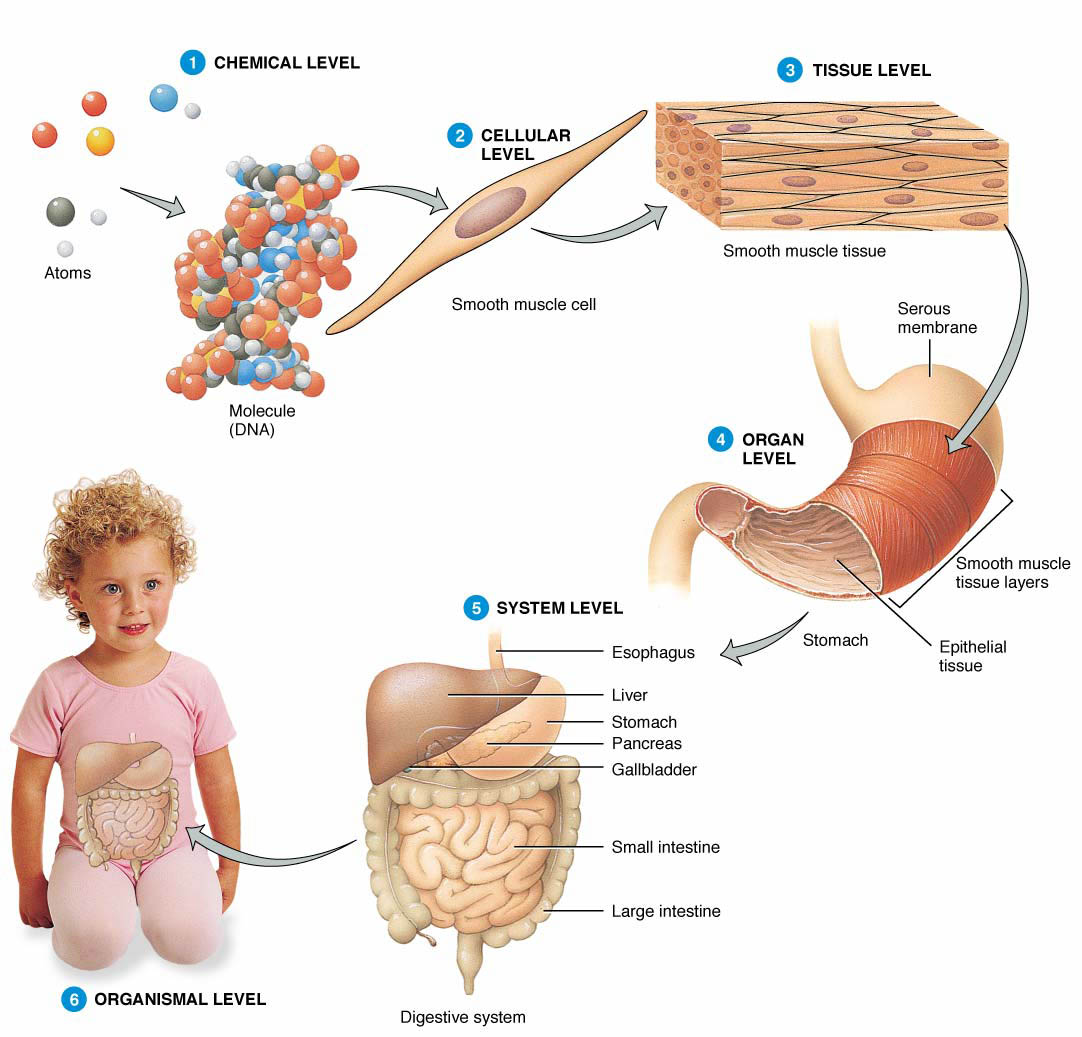
The human body has 6 main levels of structural organization. We will begin this lesson with the simplest level within the structural hierarchy.
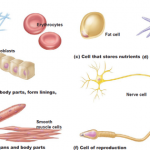
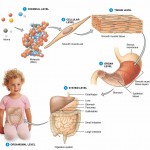
Chemical level– is the simplest level within the structural hierarchy. The chemical level includes the tiniest building blocks of matter, atoms, which combine to form molecules, like water. In turn, molecules combine to form organelles, the internal organs of a cell.
Cellular level– the cellular level is made up of the smallest unit of living matter, the cell. Individual cells may have some common functions but vary widely in size and shape. Each type of cells carries out a set of unique tasks within the human body.
Tissue level– Tissues are groups of similar cells that have a common function. A tissue must contain two different types of cells. The four basic tissue types in humans include epithelium, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. Each tissue has a characteristic role within the human body which we will discuss later.
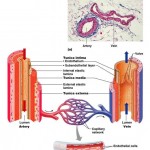
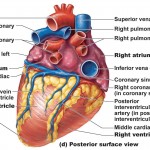
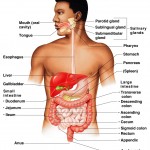
Organ level– an organ is a structure composed of at least two different tissue types that perform a specific function within the body. Examples include the brain, stomach, and liver. Complex functions begin to emerge at this level.
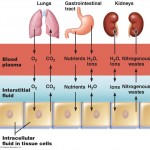
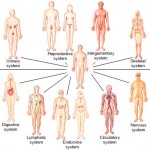
Organ system level– One or more organs work in unison to accomplish a common purpose. For instance, the heart and blood vessels work together and circulate blood throughout the body to provide oxygen and nutrients to cells. Besides the cardiovascular system, the other organ systems of the body are the integumentary, skeletal, nervous, muscular, endocrine, respiratory, lymphatic, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems.
Organismal level– The organismal level is the highest level of organization. It is the sum total of all structural levels working together. In short, it is the human being (or organism) as a whole.
Review
- Name the six different levels of structural organization in the human body and explain their relationships.
- List the 11 organ systems of the human body and explain their major functions.
Check your understanding
- In the hierarchy, at which level of structural organization would a cytologist’s field of study be considered?
- What is the correct structural order of the following terms: atom, organ, cell, organism, tissue?
- Which organ system includes the heart and blood vessels? Which organ system includes the kidneys?
Related Posts
Category: The Basics

Nice
I am very happy to have this site right at my finger tips. it is making my walk of medicine so easy. love it too much and will continue commenting as I continue using it. keep it up.
I just stumbled upon this website and my oh my it has been a life saver already. I love how it gives an easy to read explanation. It’s been helping me prepare for the HESI A2 exam and for nursing school!
The levels are listed in bold I. Chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and organism.