Archive for July, 2014
Lever Systems: Bone-Muscle Relationships
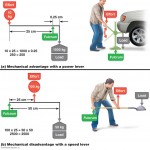
How do our bones and muscles work? What makes movement possible? These are just a few questions you may find yourself thinking about now and again, and although these questions cant be answered in a single article, we can tackle the idea of leverage and bone-muscle relationships. In this article we’ll discuss mechanical advantage, mechanical disadvantage, the idea of a lever, fulcrum, effort, and load, classes of levers, and lever systems within the human body.
Muscle Mechanics: Fascicle Arrangement
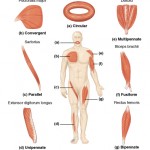
How do muscles work? Picture a hand-woven quilt full of strong fibers that have different shapes, sizes, and elasticities. The fibers may converge toward a single point, or run parallel with other muscles. Maybe they’re circular (like the muscle fibers around your mouth and eyes), and attach obliquely. In short, the arrangement of a muscle’s fiber bundles (fascicles) determines its range of motion and power. In this article we’ll discuss fiber arrangements and muscle mechanics.
Function and Classification of Bones
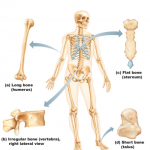
The human skeleton contains 206 known bones and because of its sheer scope, a classification system had to be invented. Typically, bones are classified into four categories by shape: long, short, flat, and irregular. The skeleton is again classified into smaller and more specific groups which we’ll discuss in future publications. The seven functions of bone: support, protection, movement, mineral storage, cell formation, fat storage, and hormone production are briefly discussed as well.
Skeletal Cartilages
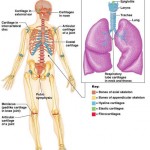
Along with its bones, the skeleton contains resilient cartilages, and although the major focus of this category is skeletal structure and bone tissue, we will briefly discuss the three main skeletal cartilages in this article. Skeletal Cartilages The human skeleton is initially made up of cartilages and fibrous membranes, but bone soon replaces most of […]
Cell Junctions
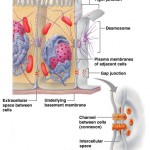
Cell Junctions Although certain cell types – blood cells, and some immune system cells – move freely in the body, many others are packed into tight communities. Typically, three factors act to bind cells together. Glycoproteins in the glycocalyx act as an adhesive. Contours in adjacent cells membranes fit together in a tight knit fashion. […]
The Plasma Membrane: Structure
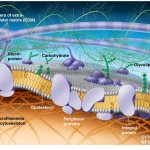
Plasma Membrane The flexible plasma membrane defines the barrier of a cell by separating two of the body’s major fluid compartments – the intracellular fluid within cells and the extracellular fluid (ECF) outside cells. The term cell membrane is commonly used as a synonym for plasma membrane, but in this article we will refer to […]
Cell Theory: The Cellular Basis of Life
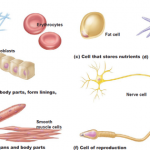
Cell Theory In the late 1600’s, an English scientist named Robert Hook was the first to observe plant cells with a crude microscope. Then, almost a century and a half later, in the 1830’s two German scientists proposed that all living things are composed of cells (Their names were Mathias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann). A […]