Archive for May, 2013
Chemical Bonds
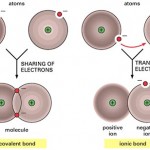
Chemical Bonds When atoms combine with other atoms they are held together by chemical bonds (bonds formed between electrons of reacting atoms). These electrons occupy regions of space orbiting the nucleus called electron shells. Each electron contains one or more orbitals and each electron shell represents a different energy level (a general understanding of chemical […]
Molecules and Compounds
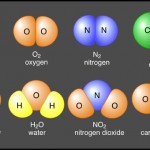
Molecules and Compounds In a recent article we discussed the importance of atoms and elements, but most atoms do not exist in a free state. Instead, they combine with other atoms through chemical bonds forming molecules and compounds. A molecule is a group of two or more atoms from the same element held together by […]
Atoms and Elements

Atoms and elements All matter is composed of elements. An element is a structure that cannot be broken down into simpler substances (by ordinary methods). Some well known elements include oxygen, carbon, and iron. Currently, science recognizes 118 elements, 92 occur in nature and the other 26 are made artificially. 96% of the human body […]
Basic Chemistry: Matter and Energy

Matter and energy You may be asking yourself, what role does chemistry play in anatomy and physiology? Well, the answer is fairly simple. Your entire body is made up of 1000s of chemicals that continuously interact with one another. Since chemical reactions are a part of all physiology processes within the body, a basic understanding […]
Body cavities and membranes
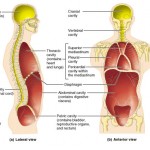
Body cavities and membranes In most cases, the body is described as having two main cavities called the “dorsal and ventral body cavities”. Some anatomical references do not recognize the dorsal body cavity but we will use it in this example because it’s used by many professionals and colleges. It also makes it easier to […]
The Language of Anatomy: anatomical position and directional terms
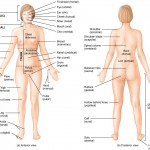
Anatomical position and directional terms The healthcare industry has its own terminology, especially anatomy and physiology. In order to provide exquisite care and understand the inner workings of the human body, anatomical terminology is a necessity. We’ll begin by going over “anatomical position and directional terms”. In order to describe body parts and positions correctly, […]
Homeostasis: positive/ negative feedback mechanisms
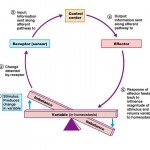
If you study biology or medicine, having a solid understanding of homeostasis is extremely important. All living systems are based on maintaining an internal environment and equilibrium. In homeostasis, positive and negative feedback mechanisms balance inputs, outputs, and responses. Most control mechanisms use a negative feedback loop, but some, like childbirth would be considered positive feedback.
Human Body Organ Systems: An Orientation
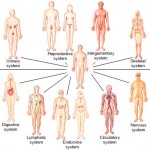
Can you name the 11 organ systems of the human body from memory? If not, this may be a good refresher read for you and a great place to start for beginners! In this article, we review and discuss the 11 organ systems of the body. The main focus is anatomy and which organs makeup each particular organ system, but we will briefly discuss each organ systems main function and role within the body also.
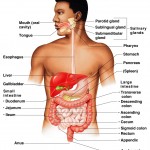
Maintaining Life: Necessary Life Functions

Necessary Life Functions We recently discussed the structural levels of the human body. Next, we’ll take a look at what it actually does. Like all complex animals, humans must maintain a core set of necessary life functions to survive. These include maintaining boundaries, movement, responsiveness, digestion, metabolism, excretion, reproduction, and grow. Many people try to […]
A&P: Levels of structural organization
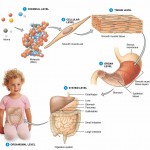
One of the basic concepts in anatomy and physiology is the idea of organization. Levels of structural organization in the human body work from simple to complex, or small to large. For instance, the simplest level, or “chemical level”, consists of atoms and molecules. The highest and most complex level of organization, the organismal level, represents the sum total of all structural levels working together in unison.